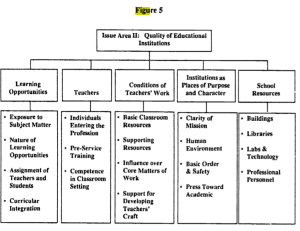
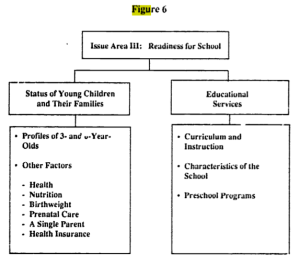
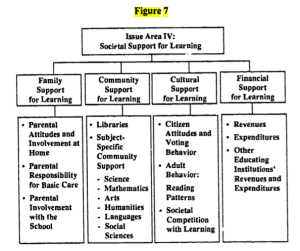
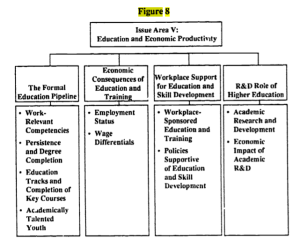
Wow! It took this crap-fest of a presidential election to get the issue of foreign influence to the national stage. But seriously, we actually do need to talk about foreign influence in the inner workings of our government —in the making of our laws.
Sure, we should be appalled by foreign governments trying to influence our elections but foreign influence in our government is nothing new; it’s business as usual in the cesspool of Congress. 
Oh, and I might as well be upfront with you. This blog isn’t about the presidential election. This is about BIG money in politics. This is about foreign interference in our lives on a regular basis.
So please, hang with me on this little, but disgusting, story. You need to know how multinational corporations stealthily exert foreign influence on Congress and pilfer our coffers. And even worse, the villains in this story are quietly working to privatize a whole public system and create a global monopoly on education. (Hidden Privatisation) TRUE STORY!
The story begins with the British-owned company Pearson Education Corporation. They aren’t the dreaded Russians but they are a foreign influence none-the-less.
Pearson provides publishing and assessment services to corporations and schools from Pre-K to higher education and …. professional learning (oh, that’s a story for another day!).
Do they influence our public policies through lobbyists? Yes, openly.
Sandy Kress, the controversial testing lobbyist, was the architect of No Child Left Behind who then lobbied for Pearson Education while simultaneously serving on several state advisory boards. Kress became so unpopular amid an anti-testing rebellion in Texas that the legislature made it illegal for him or any other testing lobbyist to make campaign contributions. Even registered sex offenders can give politicians money in Texas.
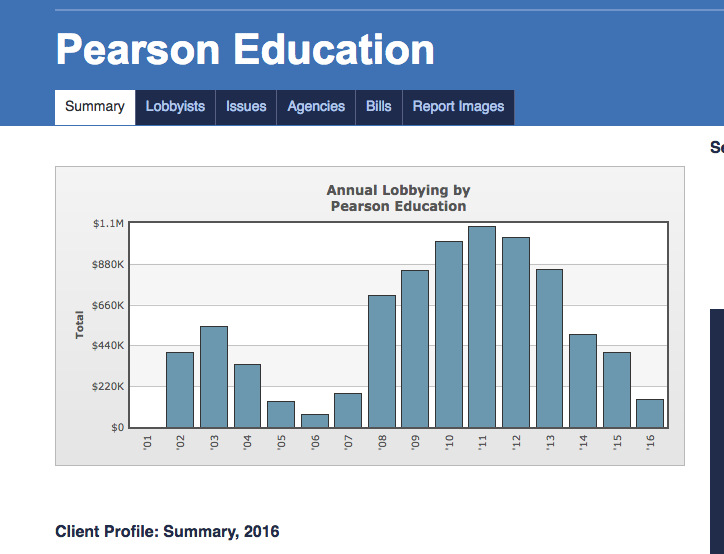
Provided by Open Secrets
Pearson’s lobbying of Congress increased just after the writing of No Child Left Behind in 2001 and Common Core in 2008. Remember, this is foreign influence over dollars spent. They secure the law then secure the spending.
It’s legal. But it’s not right.
And it’s the stealthy part of this story that should really alarm us —the think tanks.
Think tanks influence the actual writing of the laws. Foreign powers do buy influence through them. Their goals become the aim of our laws. Terminology is of their choosing. Their influence fixes a law in place. That’s how the development of “an industrial complex” works — by influencing “public” policy. (“Public” in the sense that the public follows the law.)
And unbeknownst to most of the public, it can be foreign agents creating the loopholes that keep us running in circles unable to ever catch up to the truth in time. The money’s pocketed before we know it.

Defining the Education-Industrial Complex
But, let’s get back to the story. We know this…
Pearson announced “in the summer of 2000 to spend $2.5 billion on an American testing company.” (Some thought it wasn’t a great investment. Ha!)
…“the next year, Congress passed the No Child Left Behind Act, which mandated millions of new standardized tests for millions of kids in public schools.”
Pearson just happened to be “in a prime position to capitalize.”
And we know…
School testing corporations have spent at least $20 million on lobbying along with wining and dining or even hiring policymakers in pursuit of big revenues from federal and state testing mandates under “No Child Left Behind” measures and the Common Core curriculum, according to a new analysis by the Center for Media and Democracy (CMD).
Yup. Lawmakers created a no profit left behind free-for-all targeting public school children.
Now, this is the point in this little story where the connection of Pearson to Marc Tucker—the unofficial consultant for our fundamental change to a standards-based (test-based) system under No Child Left Behind —was still only speculation in my mind….until I found the following fact.
On Sept. 10, 2001, President George W. Bush was at Jacksonville, Florida’s Justina Road Elementary School “to tout his $900 million education agenda.” He…
“chose Justina because test scores at the Duval County school have steadily increased in the past few years, thanks to a new program that emphasizes literacy skills.
That program – America’s Choice.”
ALWAYS, the plan was sold using this promise…
“Every student should leave high school capable of doing college-level work without remediation.”
These same words were in my states’ mission for “our” standards-based accountability system in 1999 and the words were reused again to sell Common Core. Is No Child Left Behind connected to Common Core in the minds of most Americans?
Is the choice of words, a coincidence? No. The connection is America’s Choice.
Tulsa Public Schools (TPS) first partnered with America’s Choice in May 2009. Financed with more than $3 million in federal Title I funds from the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act, America’s Choice is working with the district to implement the Rigor and Readiness Initiative into 19 middle and high schools. The initiative, which America’s Choice developed with ACT Inc., the company that creates the college preparation test, includes the Ramp-Up and Navigator curricula.
The Common Core State Standards Initiative was also funded with money from the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act. The think tanks and other “education organizations” got together. And the same people continue to profit from selling us the same product (the standards & testing-based theory)— repackaged.
Funded with American Recovery and Reinvestment Act dollars!?!!!?!! In the Great Recession our Recovery Act dollars fed the multinational education industry…. foreign companies instead of our children. Wall Street at the expense of Main Street! Wasn’t that the outcry?
So who founded America’s Choice? Marc Tucker. What think tank does he run? National Center for Education and the Economy (NCEE). How influential is he? Way, way too influential.
When it comes to education law, if parents and teachers were half as influential as this one man, we might actually get to the promised land — equal educational opportunity.
Ah, but the rest of the story —the Coup de grace $$$$$$$$$$
America’s Choice…
“began as a program of the National Center on Education and Economy (NCEE) in 1998 and became a private [for-profit] organization in 2004.”
…combined with Pearson…to seal the deal.
Pearson and America’s Choice Announce Acquisition Agreement
August 3, 2010 —Pearson…today signed a letter of agreement to acquire America’s Choice…Pearson’s extraordinary resources and technological expertise will facilitate the adaptation and reach of America’s Choice’s comprehensive and proven school improvement model to a global community of educators and students.
What do you think America? What’s America’s choice?
America’s choice isn’t high skills or low wages like Mr. Tucker says in his propaganda.
America currently has no choice. We are at war; it’s money-driven law versus people-driven policies.
 You think that when domestic influences (think-tanks) team up with foreign-born companies, they are unstoppable? Absolutely not.
You think that when domestic influences (think-tanks) team up with foreign-born companies, they are unstoppable? Absolutely not.
But we have to face the facts.
Both political parties are corrupted to the core. And every person voting to return their boy or girl to congress is voting for more of the same. You want change. Change Congress.
You want revolution. Start with a peaceful tactic — revolt at the voting booth. Be the anti-incumbent vote. Then rise to the challenge of beating back the testing machine in your own schools.
Such a deplorable, revolting situation as allowing foreign corporate-created laws to control the education of U.S. children is intolerable. It ends with us.