The National Governor’s Association (NGA), corporate leaders, foundations and other special interest groups advanced a clear plan to use the rise of the Information Age to float the economy. Their vessel? Our public education system.
Necessary or not, the school policy revolution began.
1969 — 75% of parents sampled (PDK/Gallup) said they would like to see one of their children teach in a public school.
1979 — 86% of parents with children 13 years and older had no desire to send their children to a different public school.
 1983 — Governor Lamar Alexander created TN’s “Better Schools Program,” which put a merit pay system (pay for performance/career ladder) at the heart of the plan.
1983 — Governor Lamar Alexander created TN’s “Better Schools Program,” which put a merit pay system (pay for performance/career ladder) at the heart of the plan.
The hook: the idea of “flexibility” in exchange for “results.”
The pretense of accountability in an outcome-based (pay-for-results) system was launched ahead of the Reagan administration’s report A Nation at Risk.

6-14-1983 President Reagan participating in a Regional Forum on the National Commission on Excellence in Education Report with Governor Lamar Alexander at the Farragut High School in Knoxville, Tennessee
The Test-Based Accountability Ship Sailed
Demand for testing needed to be created but a couple of barriers stood in the way — local control and an established and effective education system. So a clear plan to take over school policy needed to begin with a strategy to undermine the public’s trust in the institution of public education. This was known:
Parents know a good deal more about the schools … than nonparents. They are heavily influenced by firsthand knowledge, whereas the opinions of nonparents derive more often from the media,… (PDK/Gallup 1984)
The larger voting block — non-parents — became the first target for an information campaign.
1986:
“When the Carnegie Forum Task Force began its work, we knew that the Governors were the key to the necessary revolution in school policy.”
Marc Tucker —1986— then executive director of the Carnegie Forum on Education and the Economy
With Governor Lamar Alexander chairing the NGA, they released a report titled Time for Results.
The Reagan administration supported the clear plan to support the education industry.
“What is industry in a knowledge-based economy?” The answer is the education industry.
Lewis Branscomb —1986— IBM Chief Scientist, Head of Carnegie Foundation Task Force on Teaching
The education industry would profit from two main concepts, outcome-based education and “school choice.” But the establishment of national standards were essential for industry “efficiency,” or to reach “economies of scale” (higher return on investment). National standards provided a national foundation for large-scale operations.
The Course was Set: “Education Reform.”

This project was under the direction of Secretary of Education William (Bill) Bennett with assistance from his political bedfellow, Governor Lamar Alexander.
1987 — With Governor Alexander navigating both state and federal policy waters, the governors floated projects in several states with 1991 as the target date for reporting the results. Supposedly “the results” would determine if these “real reforms” should be scaled-up nationwide. Trustworthy analysis was crucial.
It appeared that our national research and development system—Regional Education Laboratories— put in place under the 1965 Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) — would be central to that research.

In addition to our Regional Educational Laboratories, the Research and Development (R&D) Centers are also part of our U.S. R&D system.
1988 — Before leaving office, Reagan signed the Hawkins-Stafford Amendments to ESEA.
Including: “requirements regarding accountability evaluation of programs conducted in accordance with national standards to be developed by the Department of Education.”
Boundaries Were Crossed
That policy change took ESEA from a law that prohibited any federal influence over curriculum and instruction to placing evaluation of programs associated with national standards under the direction of the Secretary of Education. Not just schools, but the whole governing structure of schools was to be restructured, not just reformed.
“Restructuring” Schools: Creation of the School to Workforce/Military Pipeline
1989—Marc Tucker advised President-elect Bush about the education restructuring efforts underway by businesses and the NGA.
Tucker’s own organization, National Center on Education and the Economy (NCEE), created the National Alliance for Restructuring Education (NARE) to promote Standards-Based Education. And…
… privately, an education summit was planned. New NGA chairman, Terry Branstad, hoped “the focus of the meeting would be on tailoring our education system for the workforce of the future.”
The first (invitation only) National Education Summit was held for the president with governors, business leaders, and a few representatives.
A joint statement confirmed that the setting of national goals and the development of “a system of accountability that focuses on results” had been agreed to.
 1990— Tucker’s (NCEE) publication of “America’s Choice” continued the push for policies to focus on output measures (hear Tucker explain beginning at minute 33:30) as Governor Bill Clinton summarized …
1990— Tucker’s (NCEE) publication of “America’s Choice” continued the push for policies to focus on output measures (hear Tucker explain beginning at minute 33:30) as Governor Bill Clinton summarized …
“We need a national exam, measured by international standards, and the continued development of a quasi-governmental institution.”
A Quasi-Governmental Institution? As that sinks in, please keep reading.
1991— President George H.W. Bush appoints Lamar Alexander as his second Secretary of Education.
 With Alexander in charge, and his Office of Educational Research and Improvement (OERI) being the “lead agency” for research, the nation should have heard results from Project Education Reform: Time for Results. Instead, the nation got a report card.
With Alexander in charge, and his Office of Educational Research and Improvement (OERI) being the “lead agency” for research, the nation should have heard results from Project Education Reform: Time for Results. Instead, the nation got a report card.
The results? This New York Times reporter gives us some clues about Alexander’s strategies and the results.
“…disappointingly superficial on the issues…
“He resists detailed debate …”
“…and the program he’s got is not a winner, …”
The Alexander agenda included national standards and testing, teacher merit pay, change through competition, and “choice.”
The “Education Council Act of 1991” established a temporary 32 member council — National Council on Education Standards and Testing (NCEST) — “most of whom were appointed by the Secretary of Education.”
1991 also marked the nation’s first voucher legislation (proposed by Secretary Alexander).
1992 —No surprise. NCEST recommended national standards and testing. But it was without answering some important questions and …
“NCEST does not explain why the proposed tests will not narrow the curriculum.” Daniel Koretz & Others
1992— President Bush lost his re-election bid to Bill Clinton.
Marc Tucker penned his infamous November 11, 1992 letter to Hillary Rodham Clinton.
“Tucker’s plan would change the mission of the schools from teaching children academic basics and knowledge to training them to serve the global economy in jobs selected by workforce boards.” Thinker, RealistNews
Presidents Changed: The Politically Powerful Continued the Policy Journey
“To remold the entire American system for human resources development.” Marc Tucker
1993— D.C. think tank “Empower America” was co-founded by former Reagan Education Secretary William (Bill) Bennett.
Empower America philosophy: “…opportunity, competition, ownership, and freedom—must be the framework for reform of century-old public systems such as K-12 education, the tax code, and social security.”
1994— President Clinton signed the “Improving America’s Schools Act” (IASA).
Clinton’s ESEA reauthorization -IASA;
- mandated accountability based on grade-span (3rd,8th,11th) standardized testing,
- called for content standards to be set by ALL states, and
- added funding for charter schools into ESEA for the first time.
Meanwhile, Lamar Alexander became a co-director of Empower America.
“We’re planning on [Mr. Alexander] coming back and being a part of a big school-choice initiative.” Empower America
1996-2002 — The school policy revolution shifted to state efforts to expand outcome-based accountability mechanisms (exit-standards testing) and charter schools.
Remember, industries were counting on public education money and governors were always key to the “necessary” school policy revolution.
“The role of the governors … was crucial because they mobilized the public and legislators in their states to support educational reforms.”
The Technology Industry Took the Helm
1996 — The Education Summit, as the story goes, gave birth to the Gates’ supported Achieve, Inc.
1997 — Lamar Alexander & Bill Gates addressed the NGA. Alexander mused about how after all the years of governors “leading the charge” and pouring money into “their plan,” charters and standards had not improved education.
1998 — Tucker’s NCEE created the “America’s Choice School Design Program” (later purchased by Pearson Inc.).
1999 — Tucker’s NCEE launched the National Institute for School Leadership (NISL) and Bill Gates launched the “Gates Learning Foundation.”
NCEE was asked by Carnegie Corporation, joined by the Broad Foundation, the Stupski Foundation and the New Schools Venture Fund, to create a design for a new kind of national organization to train school principals to lead high performing schools.
Time to Drop Anchor on The Nation

2002: The Broad Academy was founded. Source: The Christian Science Monitor
2002 — The 2001 President George W. Bush’s ESEA reauthorization, No Child Left Behind (NCLB) went into effect.
Among other things, NCLB:
- expanded standardized testing to yearly (3rd-8th grade and once in high school),
- required ALL students be “proficient” on state tests by the 2013-14 school year,
- promoted and assisted states in “enhancing” achievement through technology,
- expanded “school choice” through a variety of programs (Clinton era – $15 Million expanded to $214.8 Million by 2007. Now, FY2018 $1.4 Billion “for public & private school choice opportunities” ),and NCLB
- allowed access to student data for military recruiters.
In addition to NCLB’s passage, the Education Sciences Reform Act of 2002 changed the federal system of research, development and dissemination of educational practices by created Comprehensive Centers (Regional and Content Centers).
Failure to get results from standards (Outcome-Based Theory) and “choice” had been blamed on being “too timid,” the addition of federal CENTERS worked to more aggressively implement the agenda. Instead of functioning to meet regional needs like the Regional Educational Laboratories originally did, these centers are being used to “provide frontline assistance.” For example, they were used to implement the Common Core Initiative, an initiative designed and controlled by a quasi-governmental organization.
Last but not least of the 2002 policy anchors, the Educational Technical Assistance Act of 2002 established the Statewide Longitudinal Data Systems (SLDS).
Full Speed Ahead
2003 — Lamar Alexander began his senate career.
2005 — Having been recognized as the most influential person in School Policy, Bill Gates co-chaired the National Education Summit.
2006 — The Data Quality Campaign (DQC) Launched at the Data Summit.
The campaign promoted the Gates’ “ten essential elements” of a longitudinal data system, which included the ability to match student records between the Pre-K and post-secondary systems.
2007 — NO CHILD LEFT BEHIND should have been left behind. (ESEA review & reauthorization IS required every 5-6 years, by law.) NCLB remained anchored in place while common standards and assessments were being “piloted.”
2008 — Idaho was the last state to complete a statewide longitudinal data system with all the elements required by Gates’ DQC.
Meanwhile, unofficial “reports” declared an educational crisis in cities while the Great Recession disrupted the nation.
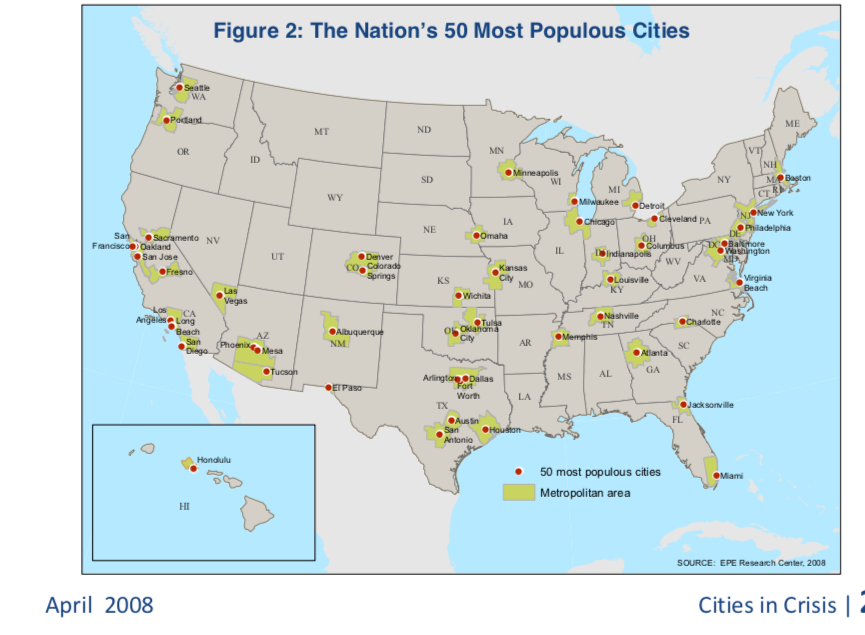
For me, this map represented the War Plan. I watched as city schools and family’s lives were disrupted with school closures. This “report” was prepared with support from America’s Promise Alliance and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation
The Race Begins
2009 —Oh what a year! 43 percent of all large urban superintendent openings were filled by Broad Academy graduates.

In the Education Reform Toolkits by The Broad Foundation.
The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 went into effect and the quasi-governmental institutions went to work on spending those funds.
Race to the Top began: “And finally, for the first time in history, we have the resources at the federal level to drive reform.”
Bill Gates explained at the National Conference of State Legislatures (NCSL) that a thorough data collection system is the best way to track student success.
2010 — Common Core became a common problem.
The Workforce Data Quality Initiative began granting federal money to connect education and the workforce data.
 2011 — The undercurrent of revolt against outcome-based policies —high-stakes testing and the “accountability” systems based on them— began to surface. The resistance organized; we marched and we met.
2011 — The undercurrent of revolt against outcome-based policies —high-stakes testing and the “accountability” systems based on them— began to surface. The resistance organized; we marched and we met.
 2012 —The Obama administration called for Congress to “reform NCLB” but instead the nation got accountability waivers in exchange for adoption of “more honest standards.” Honestly, “college and career ready standards” meant the Common Core standards.
2012 —The Obama administration called for Congress to “reform NCLB” but instead the nation got accountability waivers in exchange for adoption of “more honest standards.” Honestly, “college and career ready standards” meant the Common Core standards.
2013 — The NCLB replacement the “Every Child Ready for College or Career Act” was introduced by Senator Alexander.
2014 — Revolts against the college, career and military ready Common Core National Standards grew.
2015 — Lamar Alexander took over the chairmanship of the Senate education (HELP) committee and introduced a new name for the NCLB replacement, “The Every Child Achieves Act,” which later became the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) we now have as our ESEA reauthorization. Is ESEA better than NCLB? You decide.
The flaws in No Child Left Behind remain. The funding for testing, technology and school choice are increased.
Clear Sailing to the Finish Line of the Revolution in School Policy
?
The finish line? A quasi-governmental organization controlling common national standards and testing with all data collection and consolidation in a single office for use in the Workforce Placement System.
A “computer-based system for combining this data” was always central to the Tucker Education-Labor System Plan.
The Foundations for Evidence-Based Policymaking passed as HR 4174 (sponsored by Speaker Paul Ryan) but its identical sister bill was sponsored by Gates’ Washington State Senator Patty Murray.——–2019——–signed into law by President Trump.
This “honestly” is a bipartisan revolution in school policy
 The Outcome of the School Policy Revolution?
The Outcome of the School Policy Revolution?
54% of Americans say they would NOT want their child to become a public school teacher, a majority for the first time in a question initially asked in 1969.
70% of parents still give their oldest child’s school an A or B grade.
The Republic? Creeping or Leaping Towards Totalitarianism.
Lamar Alexander has consistently claimed to support “local control,” but what is left to control?
#####
For those requiring more proof of these historical events, more detailed of educational results, or the references not already provided, please review (and download for free) the journal article Assessing the Cornerstone of U.S. Education Reform.